President Barack Obama pushed forward a national health care plan to increase the availability of medical care for all Americans. How would one determine the opportunity cost of the proposal?
Every decision by government has an opportunity cost, as would any decision made by consumers or businesses. One would have to determine the best forgone alternative, be it national defense, a space station, the Superconducting Super Collider, the environment, or a tax cut. Each of these has a "value," even if it is hard to put a price tag on it. Clearly, determining the opportunity cost of such a complex decision is not easy in practice.
You might also like to view...
What could explain why a decrease in taxes could lead to a less-than proportionate increase in output ?
A. Consumers may choose to save much of the tax cut in anticipation of having to pay higher taxes in the future. B. As a result of diminishing returns to current consumption, consumers may choose to spread the extra spending over the long term rather than consuming the proceeds of a tax cut all at once. C. A decrease in taxes will necessitate lower government outlays, thus largely offsetting the higher consumption expenditures of households. D. All of the above. E. A and B only
Exhibit 30-3 Costs of Eliminating:Firm A Firm B Firm C 1st ton of pollution$ 30 $ 50 $ 600 2nd ton of pollution$ 70 $ 90 $ 700 3rd ton of pollution$125 $150 $ 900 4th ton of pollution$200 $250 $1,300 Refer to Exhibit 30-3. What is the cost to Firm B of eliminating 2 tons of pollution?
A. $350 B. $250 C. $300 D. $140 E. $540
International trade in the U.S. during the antebellum period
(a) benefited the Northern economy more than the Southern economy. (b) benefited England significantly more than the U.S. (c) played an important part in the growth and expansion of the Southern economy. (d) occurred as described in all of the above.
With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers:
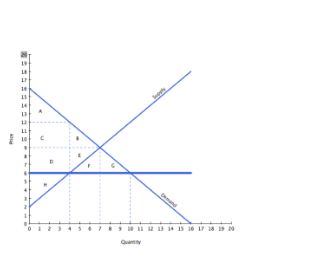
A. then the policy was effective since consumers gained in surplus overall.
B. then the policy was ineffective since consumers gained in surplus overall.
C. then the policy was ineffective since consumers lost surplus overall.
D. then the policy was effective since consumers lost surplus overall.