In Brazil, the longest period of daylight occurs during the month of
a. December. c. September.
b. March. d. June.
A
You might also like to view...
Newtonian physics tells us that Kepler's second law is a result of the conservation of ____
a. angular momentum b. linear acceleration c. energy d. mass e. velocity
assume that the surface of the storage vessel has an absorptance (equal to the emittance) of 0.1. Then determine the rate of evaporation of the liquid oxygen in kilograms per second and pounds per hour, assuming that convection can be neglected. The heat of vaporization of oxygen at –183°C is 213.3 kJ/kg.
GIVEN
• A spherical vessel of liquid oxygen in a large black room
• Emittance of vessel surface (?) = 0.1
• Liquid oxygen temperature (To) = –183°C = 90 K
• Sphere diameter (D) = 0.3 m
• Room wall temperature (Tw) = 27°C = 300 K
• Heat of vaporization of oxygen (hfg) = 213.3 kJ/kg
FIND
(a) The rate of radiative heat transfer (qr) to the liquid oxygen in W (b) The rate of evaporation of oxygen (mo) in kg/s
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state prevails
• The temperature of the vessel wall is equal to the temperature of the oxygen
• Convective heat transfer is negligible
SKETCH
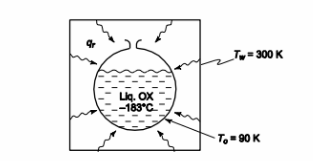
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 ? 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
This diagram represents a simplified model of the celestial sphere. The unlabeled circle that is highlighted in purple represents
A) the celestial equator. B) the meridian. C) the ecliptic. D) the spring equinox.
Three boxes in contact rest side-by-side on a smooth, horizontal floor
Their masses are 5.0-kg, 3.0-kg, and 2.0-kg, with the 3.0-kg box in the center. A force of 50 N pushes on the 5.0-kg box, which pushes against the other two boxes. (a) Draw the free-body diagrams for each of the boxes. (b) What magnitude force does the 3.0-kg box exert on the 5.0-kg box? (c) What magnitude force does the 3.0-kg box exert on the 2.0-kg box?