During synaptic transmission,
A) The frequency of the action potential is directly correlated with neurotransmitter release.
B) The frequency of the action potential is inversely correlated with neurotransmitter release.
C) The intracellular concentration of Ca2+ remains stable because of intracellular buffers.
D) The concentration of Ca2+ is inversely related to the amount of neurotransmitter released.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A sarcomere is defined as the distance from one _____ to the next adjacent ____ . (The same answer fills in both spaces.)
A. Z disc B. I band C. H zone D. A band E. M line
Events of excitation contraction coupling, such as the release of calcium from intracellular stores, occur during the ________ period of a muscle twitch
A. relaxation B. contraction C. latent
Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
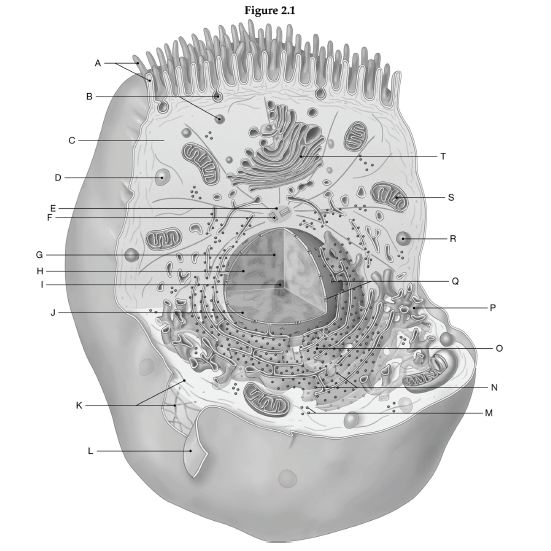
1 Label A: ______________________________
2 Label B: ______________________________
3 Label C: ______________________________
4 Label D: ______________________________
5 Label E: ______________________________
6 Label F: ______________________________
7 Label G: ______________________________
8 Label H: ______________________________
9 Label I: ______________________________
10 Label J: ______________________________
11 Label K: ______________________________
12 Label L: ______________________________
13 Label M: ______________________________
14 Label N: ______________________________
15 Label O: ______________________________
16 Label P: ______________________________
17 Label Q: ______________________________
18 Label R: ______________________________
19 Label S: ______________________________
20 Label T: ______________________________
If a 0.9% NaCl (saline) solution is isotonic to a cell, then a solution of 3.5% NaCl would be
A. hypertonic to the cell. B. isotonic to the cell. C. hypotonic to the cell. D. catatonic to the cell. E. All of these choices are correct.