What do economists mean when they say ceteris paribus?
What will be an ideal response?
When speaking about the laws of demand and supply, economists want to isolate changes in price from other changes, so they assume that key factors don't change when price goes up or down. When economists say that quantity demanded will decrease, for example, as price increases, they mean that this will happen if there are no other changes that could affect quantity demanded.
You might also like to view...
The opportunity cost of an activity is
A) the dollar cost to engage in the activity. B) the value of the resources needed to conduct the activity. C) the same for all who participate in the activity. D) what you sacrifice to engage in the activity.
Refer to Figure 24-2. Ceteris paribus, an increase in the price level would be represented by a movement from
A) SRAS1 to SRAS2. B) SRAS2 to SRAS1. C) point A to point B. D) point B to point A.
Which of the following countries has the highest output per capita?
a. The United Kingdom b. The United States c. France d. Italy e. Germany
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. The amount of external benefits associated with K-12 education in this market is ________ per student.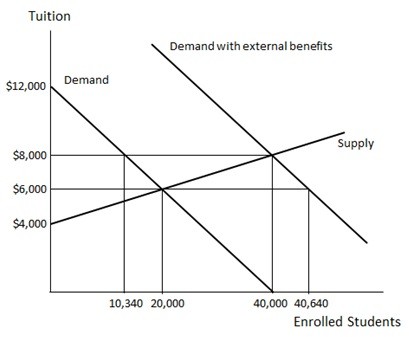
A. $12,000 B. $6,000 C. $4,000 D. $8,000