A decrease in the money supply
a. raises the interest rate, causing an increase in quantity demanded of investment and an increase in GDP
b. lowers the interest rate, causing an increase in quantity demanded of investment and an increase in GDP
c. raises the interest rate, causing a decrease in quantity demanded of investment and a decrease in GDP
d. lowers the interest rate, causing a decrease in quantity demanded of investment and an increase in GDP
e. lowers the interest rate, causing a decrease in quantity demanded of investment and a decrease in GDP
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 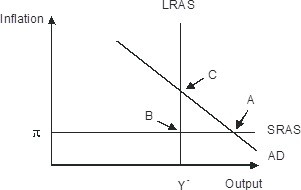
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Suppose pigs (P) can be fed corn-based feed (C) or soybean-based feed (S) such that the production function is P = 2C + 5S. If the price of corn feed is $2 and the price of soybean feed is $6, what is the cost-minimizing fee combination producing P = 200?
a. C = 100 b. S = 40 c. C = 50, S = 20 d. All points on the P = 200 isoquant would cost the same.
The mercantilism policy failed to generate gains from trade for countries which adopted it because of: a. increases in consumer spending
b. high levels of federal debt. c. supply-side shocks from the oil-exporting countries. d. runaway inflation in the U.S. e. retaliations from other countries.
The equation of exchange
A. always balances. B. usually balances. C. sometimes balances. D. never balances.