According to traditional Keynesian analysis, if the economy is in a recession, the government can move it back towards full employment by
a. cutting taxes and increasing expenditures. The effect of the tax cut is larger.
b. cutting taxes and increasing expenditures. The effect of the tax cut is smaller.
c. raising taxes and decreasing expenditures. The effect of the tax increase is larger.
d. raising taxes and decreasing expenditures. The effect of the tax increase is smaller.
b
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 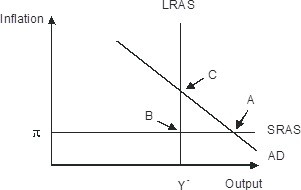
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The flaw of the Real Business Cycle model is that it
A) assumes away output fluctuations. B) assumes complete wage rigidity. C) assumes unrealistic fooling of workers. D) requires procyclical wage movements and continuous labor market equilibrium.
If a gamble has an expected value of zero, then it is termed a(n):
A. unfair gamble. B. fair gamble. C. better-than-fair gamble. D. zero gamble.
Suppose at present people hold a quantity of money equal to 85% of nominal GDP. What happens to velocity if people wish to increase their money holdings to 80% of nominal GDP?
A) Velocity can increase or decrease depending on people's tastes and preferences toward money. B) Velocity is unaffected. C) Velocity increases. D) Velocity decreases.