Your father tells you he earned a salary of $45,000 a year in 1980. This salary figure is the:
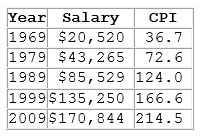
A. nominal value of his salary in 1980.
B. real value of his salary in 1980.
C. value of his salary adjusted to 2009 dollars.
D. value of his salary adjusted for inflation.
A. nominal value of his salary in 1980.
You might also like to view...
In the figure above, if the price falls from $8 to $7, demand is
A) elastic. B) inelastic. C) unit elastic. D) income elastic. E) perfectly elastic.
Let MP = marginal product, P = output price, and W = wage, then the equation that represents a situation where a competitive firm should lay off some workers to maximize profits is
A) P × MP > W. B) P × MP < W. C) MP × W = P. D) P × MP = W.
The main differences between the bank and the nonbank institutions include all of the following EXCEPT
A) banks are regulated by the Fed while nonbank institutions are not. B) banks obtain the funds to buy investment by attracting deposits while nonbank institutions borrow funds. C) banks hold more equity then nonbank institutions. D) banks' balance sheets include assets and liabilities while nonbank institutions' balance sheets include only liabilities.
Suppose we were analyzing the Turkish lira per euro foreign exchange market. If the Euro-Area's price level falls relative to Turkey and nothing else changes, then the:
a. The supply of euros in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for euros in the foreign exchange market falls, causing an appreciation of the euro. b. The supply of euros in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for euros in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an uncertain change in the value of the euro. c. The supply of euros in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for euros in the foreign exchange market falls, causing a depreciation of the euro. d. The supply of euros in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for euros in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an appreciation of the euro. e. Neither supply nor demand in the foreign exchange market change because relative international prices influence trade flows and not the exchange rate.