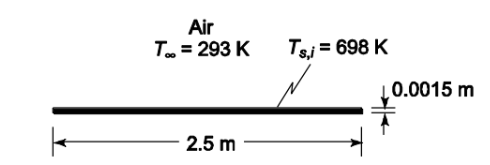
A 2.5 × 2.5 m steel sheet 1.5-mm-thick is removed from an annealing oven at a uniform temperature of 425°C and placed in a large room at 20°C in a horizontal position. (a) Calculate the rate of heat transfer from the steel sheet immediately after its removal from the furnace, considering both radiation and convection. (b) Determine the time required for the steel sheet to cool to a temperature of 60°C. Hint: This will require numerical integration.
GIVEN
• Horizontal steel sheet in air
• Sheet dimensions = 2.5 m × 2.5 m × 0.0015 m
• Sheet initial temperature (Tsi) = 425°C = 698 K
• Air temperature (T?) = 20°C = 293 K FIND
(a) The initial rate of heat transfer (q) (b) The time required for the sheet to cool to 60°C (333 K)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The room behaves as a black body at T?
• The steel sheet behaves as a black body (? = 1.0)
• Heat transfer takes place from both top and bottom of the sheet
• The steel is 1% carbon steel
• Heat transfer from the edges of the plate is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
for 1% carbon steel
Specific heat (cs) = 473 J/(kg K)
Density (?s) = 7801 kg/m3
for dry air at the mean temperature of 496 K (223°C)
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00203 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0384 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 38.7 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
(a) The characteristic length for this geometry is
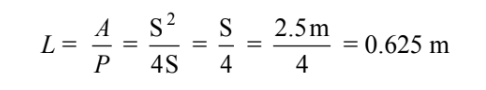
The Grashof and Rayleigh numbers are

The average Nusselt number on the bottom of the plate is given by

The average Nusselt number on the top of the plate is

The total rate of heat transfer is the sum of the convective and radiative components
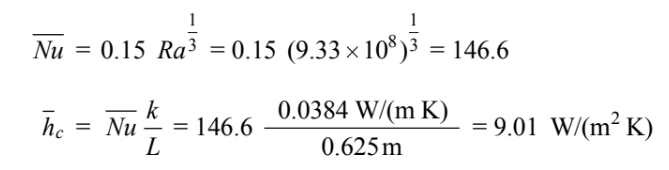
(b) As the plate cools, the rate of heat transfer will decrease. The cooling time will be estimated by calculating a new sheet temperature and heat transfer every time period.
The Biot number for the sheet is
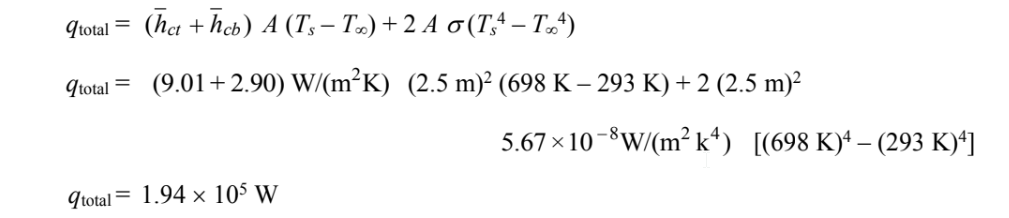
This is slightly above 0.1. For a first order approximation, we can neglect the thermal resistance in the plate. For the first 20 second interval
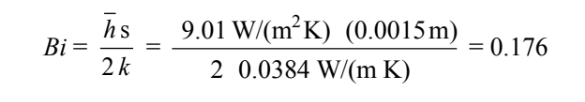
Solving for temperature after 20 sec
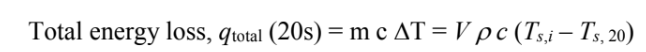
This temperature is then used to calculate new transfer coefficients and heat transfer rates as shown below. This procedure is followed until the temperature of the plate is 333 K.

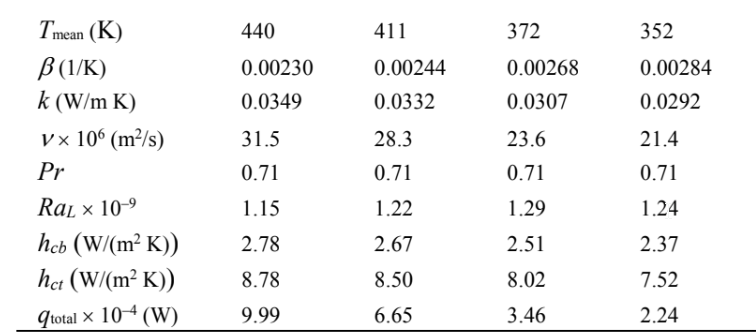
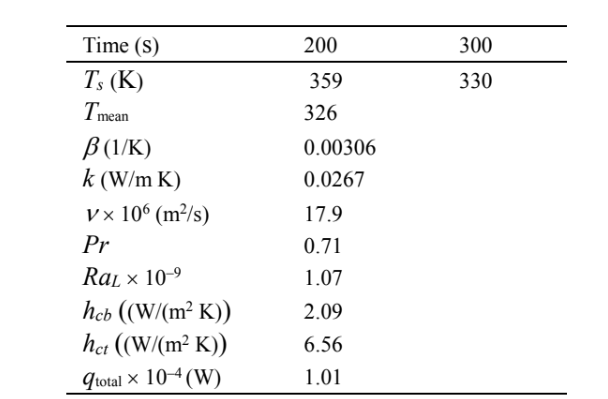
Interpolating between 200 and 300 seconds
The time required to reach 333 K is approximately 290 seconds = 4.8 min.
You might also like to view...
Parallel-Plate Capacitor: A battery charges a parallel-plate capacitor fully and then is removed. The plates are then slowly pulled apart. What happens to the potential difference between the plates as they are being separated?
A. It increases. B. It decreases. C. It remains constant. D. It cannot be determined from the information given.
According to Callicles’ presentation in Plato’s Gorgias, nature herself (in contradistinction to conventional morality) dictates that
a. the more powerful individuals should have more than the less poweful b. the community should seek to maximize the happiness of the greatest number of people c. the less powerful individuals should have more than the more powerful d. treating everybody as equals is just
A constant force is applied to an object that causes a certain displacement. If the angle between the force and the displacement is 135°, the work done by this force is
A) positive. B) negative. C) 0 J. D) Cannot be determined without knowing the magnitude of the displacement. E) Cannot be determined without knowing the magnitude of the applied force.
A straight wire of length L carries a current I in the positive z direction in a region where the magnetic field is uniform and specified by Bx = 3B, By = ?2B, and Bz = B, where B is a constant. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire?
a. 3.2 ILB b. 5.0 ILB c. 4.2 ILB d. 3.6 ILB e. 1.0 ILB