A stronger stimulus to a neuron results in ________.
A. Larger voltage changes in the graded potentials, but no changes in action potentials
B. Larger voltage changes in graded potentials and greater frequency of action potentials produced in response
C. Larger voltage changes in both graded and action potentials
D. Greater frequency of graded potentials and larger voltage changes in the action potentials produced in response
Answer: B. Larger voltage changes in graded potentials and greater frequency of action potentials produced in response
You might also like to view...
Total flow in the vertebrate circulatory system can be expressed as the total pressure change divided by
A) Total peripheral resistance. B) Total volume. C) Total length. D) Total time.
Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
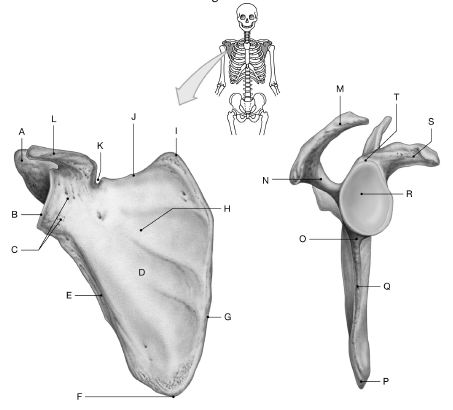
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
19) Label S: ______________________________
20) Label T: ______________________________
Which of the following muscle types are myogenic?
a. cardiac muscle b. single-unit smooth muscle c. multi-unit smooth muscle d. Both a and b e. Both b and c
The ________ pumps blood into the aorta.
A. right atrium B. right ventricle C. left ventricle D. left atrium