What benefits did an overvalued currency offer a domestic economy in the ISI period? Which sectors were typically harmed by overvalued currencies?
What will be an ideal response?
Overvalued exchange rates made it easier for targeted industries to buy imported capital goods and kept urban workers more allied with political leaders because foreign goods were relatively less expensive. It made it difficult to export, especially for the traditional commodity producers, which hurt investment and income in rural areas. Non-targeted industries lost sales and production. Industrial investment was too capital intensive and unable to create jobs fast enough to absorb labor leaving rural areas.
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large tax increase will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. recessionary; lower; potential B. expansionary; lower; potential C. expansionary; higher; potential D. recessionary; lower; lower
In a monopoly market, there is (are) ________ seller(s)
A) one B) a few C) many D) very many
Refer to the information provided in Figure 24.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.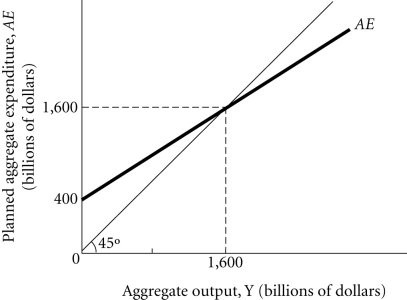 Figure 24.5Refer to Figure 24.5. If the economy is in equilibrium and the government increases spending by $100 billion, equilibrium aggregate expenditures increase to $________ billion.
Figure 24.5Refer to Figure 24.5. If the economy is in equilibrium and the government increases spending by $100 billion, equilibrium aggregate expenditures increase to $________ billion.
A. 1,700 B. 1,800 C. 2,000 D. 2,400
A monopolistically competitive firm that is incurring a loss will shut down if
A. price is less than average total cost. B. marginal revenue is less than marginal cost. C. price is less than marginal cost. D. revenues are less than variable costs.