Suppose a consumer's expected utility function given two possible states of nature A and B can be expressed in terms of consumption of food, F, in both states as U(FA, FB) = [0.6 × ln(FA)] + [0.4 × ln(FB)]. For this utility function, MUA is (0.6/FA) and MUB is (0.4/FB). Without insurance, the consumer can consume 200 in state A but only 50 in state B. The consumer can purchase insurance at a premium of 50 cents per dollar of benefit. What is the value of the insurance she purchases
A. $4.74
B. $4.85
C. $12.67
D. $114.87
C. $12.67
You might also like to view...
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD3 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: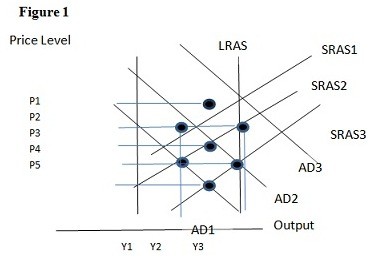
A. P3 and Y1. B. P2 and Y1. C. P2 and Y3. D. P1 and Y2.
Suppose that the marginal revenue product of labor is currently 40 and the marginal revenue product of capital is 30. If both inputs have the same cost, the firm should:
A. increase labor and reduce capital to meet the cost minimization condition. B. increase both labor and capital proportionally to meet the cost minimization condition. C. increase capital and reduce labor to meet the cost minimization condition. D. decrease both labor and capital proportionally to meet the cost minimization condition.
Suppose a firm anticipates that an R&D expenditure of $100 million will result in a new production process that will reduce costs and thus create a one-time added profit of $112 million a year later. The firm's expected rate of return is:
A. 0.12 percent. B. 112 percent. C. 12 percent. D. 2 percent.
An import quota:
A. limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus decreasing prices. B. limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus increasing prices. C. increases the amount of a good imported, thus decreasing prices. D. increases the amount of a good imported, thus increasing prices.