Why can't a firm in a perfectly competitive industry charge a price above the market-clearing price?
a. Government-imposed price ceilings prevent prices from being raised
b. Firms in a perfectly competitive industry face significant barriers to entry.
c. Perfectly competitive firms are price searchers.
d. Numerous competitors produce the same product and charge the market price.
d
You might also like to view...
Refer to the production possibility curve for Marketopia below.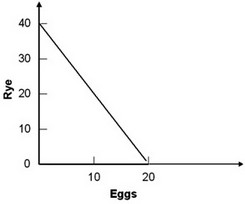 The graph indicates that with the resources and technology it has available, Marketopia
The graph indicates that with the resources and technology it has available, Marketopia
A. can produce either 40 units of rye or 20 units of eggs. B. can produce both 40 units of rye and 20 units of eggs. C. cannot produce both 20 units of rye and 5 units of eggs. D. cannot produce both 20 units of rye and 10 units of eggs.
Mergers may result in
A) anticompetitive behavior. B) more efficient production. C) fewer firms in a market. D) All of the above.
A country has a comparative advantage in the good that it can produce
a. at a lower cost in terms of other goods. b. using fewer resources than its trading partner uses. c. at a lower cost than its trading partner can produce. d. using more resources than its trading partner uses.
Which of the following exists when a market activity results in direct costs or benefits to someone who is not part of the marketplace decision to undertake the activity?
A. Externality B. Marginal cost C. Property rights D. Specificity rule