Refer to Figure 9.4. The payoffs to each firm (in billions of dollars) and an extensive form game between BP and Shell are shown in the figure. BP has 20 percent of the U.S. gasoline market share and Shell has 16 percent market share. BP and Shell are attempting to determine whether to send geologists to explore Oil Track 20.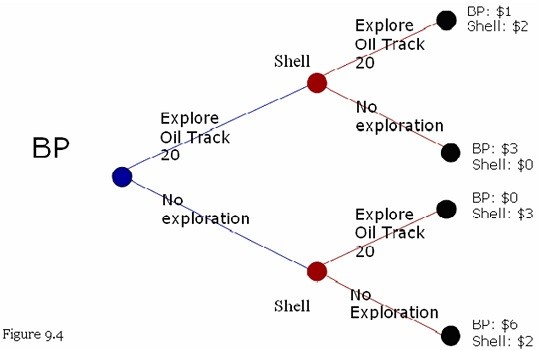 (a) Is there a dominant strategy for Shell? What is the dominant strategy, if any, for Shell?(b) What is the Nash equilibrium or equilibria in this game?(c) What is a first-mover advantage? Does BP have a first-mover advantage in this game?(d) Use the above information to advise BP on whether they should pursue a merger with Shell.
(a) Is there a dominant strategy for Shell? What is the dominant strategy, if any, for Shell?(b) What is the Nash equilibrium or equilibria in this game?(c) What is a first-mover advantage? Does BP have a first-mover advantage in this game?(d) Use the above information to advise BP on whether they should pursue a merger with Shell.
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Shell's dominant strategy is to explore Oil Track 20 because their payoffs are larger with this strategy than with no exploration.
(b) The Nash equilibrium in the game is for Shell to explore Oil Track 20, and for BP to also explore Oil Track 20.
(c) A first-mover advantage is a situation in a game where the first agent to take an action has a strategic advantage over its rivals. No, BP does not have a first-mover advantage.
(d) Yes, they could consider a merger because a merged firm could have higher profits ($8 = $2 + $6) than the combined profits from the above Nash equilibrium ($3 = $1 + $2).
You might also like to view...
The existence of marginal external benefits for a product like higher education creates a deadweight loss for society because, without government intervention, ________ would be consumed and ________ would be produced
A) more than the efficient amount; more than the efficient amount B) more than the efficient amount; less than the efficient amount C) less than the efficient amount; more than the efficient amount D) less than the efficient amount; less than the efficient amount E) the efficient amount; the efficient amount
Say's Law is the idea that
a. in the long run, the economy reaches full employment automatically b. the aggregate production function, along with the labor market, determines the economy's level of output c. total output will always exceed total spending d. whenever a good or service is produced, an equal amount of income is created e. markets always clear
If a U.S. citizen buys a car produced in Germany, this transaction will add to
a. U.S. aggregate demand. b. U.S. aggregate supply. c. German aggregate demand. d. German imports.
Which of the following is true in the short run?
What will be an ideal response?