An 20 cm-diameter horizontal steam pipe carries 1.66 kg/min of dry saturated steam at 120°C. If ambient air temperature is 20°C, determine the rate of condensate flow at the end of 3 m of pipe. Use an emissivity of 0.85 for the pipe surface. If heat losses are to be kept below 1 per cent of the rate of energy transport by the steam, what thickness of fiberglass insulation is required? The rate of energy transport by the steam is the heat of condensation of the steam flow. The heat of vaporization of the steam is 2210 kJ/kg.
GIVEN
• A horizontal steam pipe in air
• Pipe outside diameter (D) = 20 cm= 0.2 m
• Mass flow rate of steam (ms) = 1.66 kg/min=0.0277 kg/s
• Steam temperature (Ts) = 120°C =393 K
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = 20°C= 293 K
• Emissivity of pipe surface (?) = 0.85
• Heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2210 kJ/kg
FIND
(a) Rate of condensate flow (mc) at the end of 3 m of pipe.
(b) Thickness of fiberglass insulation (S) to keep loss below 1% of the energy transport by steam
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Air is still
• Thermal resistance of the convection in the pipe and of the pipe wall are negligible
• The surroundings behave as an enclosure at T?
• Insulation is foil covered, its emissivity ? 0.0
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
Thermal conductivity of fiberglass (ki) = 0.035 W/(m K)
for dry air at the mean temperature of 70°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00291 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0288 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.1*10-6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
(a) The Grashof number for the uninsulated pipe is
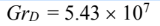
The rate of heat transfer from 3 m of the pipe( considering 1% loss in energy transport) is
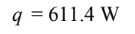
This must equal the convection from the surface of the insulation (radiation is negligible) and the conduction through the insulation.
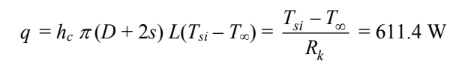
where
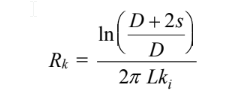
Rearranging to eliminate the insulation thickness
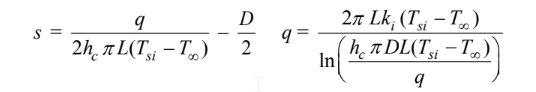
Since hc depends on the insulation surface temperature Tsi, an iterative procedure must be used. For the first iteration, let Tsi =50°C.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 35°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00323 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0261 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.1*10-6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
Assuming the insulation is thin compared to the pipe radius

Checking the units then eliminating them for clarity
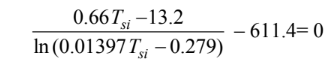
By trial and error: Tsi = 97.8°C
Performing further iterations
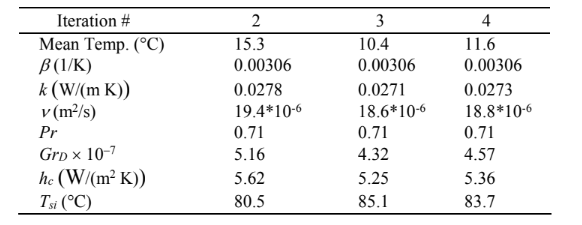
The surface temperature of the insulation is about 84°F
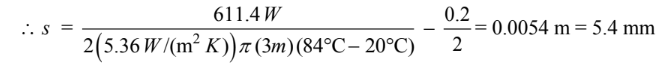
Thus about a 5.5 mm of insulation is required.
You might also like to view...
A planetary nebula has a radius of 0.5 pc and is expanding at 20 km/s. What is the approximate age of this planetary nebula? (1 pc is equal to 3×10^13 km and 1 year is equal to 3.15×10^7 seconds.)
a. 240 years b. 790,000 years c. 96,000 years d. 960 years e. 24,000 years
The most important effect in clearing the solar nebula of gas and dust was
a. impacts by planetesimals. b. the solar wind. c. the Sun's magnetic field. d. the asteroid belt. e. radiation pressure.
Solenoid: Consider an ideal solenoid of length L, N windings, and radius b (L is much longer than b). A current I is flowing through the wire windings. If the length of the solenoid becomes twice as long (to 2L), but all other quantities remained the same, the magnetic field inside the solenoid will
A. remain the same. B. become twice as strong as initially. C. become one-half as strong as initially. D. become four times as strong as initially. E. become one-fourth as strong as initially.
The major influence on the tides is due to __________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word