Consider a large open economy that has a positive current account balance. (a)Suppose the domestic government increases the tax rate on firm revenues. Draw a diagram to explain the effects on the world real interest rate, saving in each country, investment in each country, and the current account balance in each country in equilibrium. Explain your work.(b)In addition to the tax increase in part (a), suppose now that the foreign government increases lump-sum taxes on individuals. Draw a new diagram to incorporate the overall effects of both tax changes and explain the effects (from the initial equilibrium with neither tax change) on the world real interest rate, saving in each country, investment in each country, and the current account balance in both countries. Explain your work.
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | The increased tax rate on firm revenues increases the tax-adjusted user cost of capital, thus |
| (b) | If Ricardian Equivalence holds, then all the answers are the same as in part (a). If Ricardian |
You might also like to view...
If the quantity demanded for a product exceeds the quantity supplied, the market price will rise until
A) the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The product will then no longer be scarce. B) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The market price will then equal the equilibrium price. C) only wealthy consumers will be able to afford the product. D) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price will then be greater than the market price.
Happy Cows contractually requires distributors who purchase Happy Cows' milk to also purchase Happy Cows' cream. The legality of the practice will be evaluated under Section ________ of the Clayton Act.
A) 7 B) 8 C) 2 D) 3
Refer to the table below. Relative to Free Cows, the quantity that maximizes the expected profit for Happy Cows is ________ sensitive to demand changes, which makes an accurate forecast ________ valuable to the managers of Happy Cows.
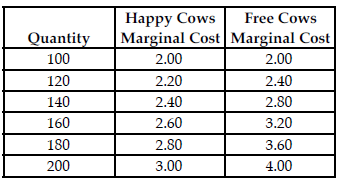
Happy Cows and Free Cows are two separate perfectly competitive dairy farms. The table above shows the respective firms' marginal cost at various production levels.
A) less; more
B) more; less
C) more; more
D) less; less
The demand curve facing Imelda's Shoe Boutique, a monopolistically competitive firm,
a. is horizontal because Imelda's is small relative to the market as a whole b. is horizontal because Imelda's is large relative to the market as a whole c. slopes downward because Imelda's is small relative to the market as a whole d. slopes downward because Imelda's sells a differentiated product e. slopes downward because Imelda's firm is the entire industry