What are the major goals that unions may pursue in labor negotiations? Are these ever in conflict with one another?
What will be an ideal response?
The most commonly held view of unions is that they seek to obtain the highest income for their members. The difficulty of describing union goals, however, is that there are trade-offs between income and employment (because of the downward-sloping nature of demand for labor). Alternative goals, therefore, include elements on job security. Unions may seek to establish and maintain seniority rules to protect jobs of long-time members; they may seek to expand the size of the union; they may seek some combination of these two extremes. While it is true that unions often have the power to raise wages above the competitive level, unions do not always exercise this power in pursuit of other goals.
You might also like to view...
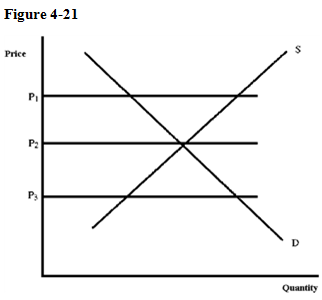
A. There will be a shortage, and the price will fall. B. There will be a shortage, and the price will rise. C. There will be a surplus, and the price will rise. D. There will be a surplus, and the price will fall. E. Equilibrium will occur in the market.
If the demand for air travel were to change so that business travelers and vacationers have the same price elasticity of demand for air travel,
A) airlines would charge the same price to each type of flyer. B) airlines would still charge business flyers a higher fare since the traveler's employer pays anyway. C) airlines would be driven out of business. D) airlines would counter by charging vacationers a higher fare.
In the traditional Keynesian model, an increase in government spending
A) causes the C + I + G + X line to shift upward by the full amount of the increase in government spending. B) causes the C + I + G + X line to shift upward by an amount less than the increase in government spending. C) causes the C + I + G + X line to shift upward by more than the increase in government spending. D) causes no change in the C + I + G + X line.
The spending multiplier is:
a. 1 / (1 ? MPC). b. 1 ? MPC. c. MPC. d. MPC / (1 ? MPC).