Exhibit 4-3 Supply and demand curves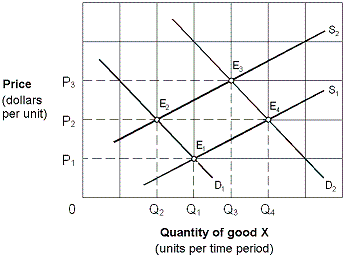
Beginning from an equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 4-3, an increase in demand for good X, other things being equal, would move the equilibrium point to:
A. E1.
B. E2.
C. E3.
D. E4.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table above. If the market for notebooks is perfectly competitive, the equilibrium price is:
A) $2. B) $3. C) $4. D) $5.
If a currency rapidly depreciates, what are the possible negative results to the economy of using contractionary monetary policy to address the depreciation?
What will be an ideal response?
With rational expectations, a correctly anticipated policy that would increase AD would lead to: a. higher inflation and lower unemployment in the short run
b. higher inflation and higher unemployment in the short run. c. higher inflation and no change in unemployment in the short run. d. lower inflation and lower unemployment in the short run.
__________________ —a term referring to the activities that businesses can perform to take advantage of economies of scale.
a. Scarcity b. Division of labor c. Core competency d. Specialization