A vector is
(a) an organism that causes disease.
(b) a disease.
(c) a substance that prevents disease.
(d) an organism that transmits a disease causing organism.
(d) an organism that transmits a disease causing organism.
You might also like to view...
Which sort of interaction is harmful to one species but beneficial to the other? What will be an ideal response?
It is known that many trees lose their leaves in response to decreasing day length. As a result, you think that Ginkgo trees may also lose their leaves in response to decreasing day length. This statement is an example of:
A. an experiment B. a hypothesis C. a theory D. deductive reasoning
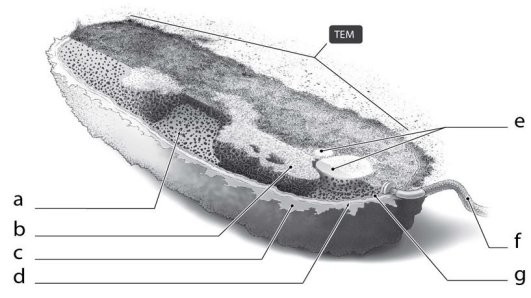 What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by "c" in Figure 3.2?
What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by "c" in Figure 3.2?
A. provide shape only B. attach to surfaces only C. protect from dehydration only D. attach to surfaces and protect from dehydration E. serve as carbohydrate storage
An important anaerobic process in the degradation of some xenobiotics is
a. oxidation by oxygenases and dioxygenases. b. cometabolism. c. microbial leaching. d. reductive dechlorination.