A single-price monopolist with a positive marginal cost will maximize profit by producing where
A. demand is price inelastic.
B. demand is price elastic.
C. demand is unit elastic.
D. Any of these may apply.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Two identical firms have access to a spring. Their marginal cost of bottling water from the spring is a constant 10¢ per bottle. The market demand for bottled spring water is P = 250 - 20Q, where P is the price (in cents per bottle) and Q is the quantity demanded (in hundreds of bottles).
(i) Suppose the two firms form a successful cartel. How much bottled water will the firms produce, and what price will they charge? (ii) Suppose the firms behave as in the Bertrand model of oligopoly. How much bottled water will the firms produce, and what price will they charge? (iii) Suppose the firms behave as in the Cournot model of oligopoly. How much bottled water will the firms produce, and what price will they charge?
Raising the personal income tax rate rotates the consumption function ________ and ________ the tax-adjusted MPC
A) downward; raises B) upward; raises C) downward; lowers D) upward; lowers
The aggregate demand–aggregate supply model shows that closing an expansionary gap involves deflation and closing a recessionary gap involves inflation
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information provided in Figure 26.8 below to answer the question(s) that follow.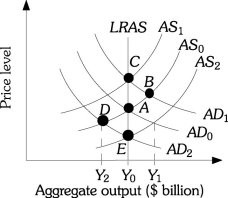 Figure 26.8Refer to Figure 26.8. If the economy is currently at Point B producing output level Y1
Figure 26.8Refer to Figure 26.8. If the economy is currently at Point B producing output level Y1
A. input prices are likely to rise. B. aggregate supply shifts to the left and the economy ends up at Point C. C. the economy is operating above full employment. D. all of the above.