The figure below shows the foreign exchange market. D£ is the nonofficial demand curve for pounds. S£ (Spring-summer) and S£ (Autumn-winter) are the nonofficial supply curves of pounds during the spring-summer and autumn-winter seasons, respectively. Assume that the British government is committed to maintaining a fixed exchange rate at $1.90 per pound. In the Autumn-winter period, what type of intervention must British monetary authorities engage in?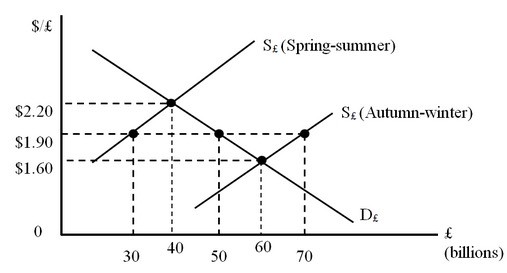
A. Buy 20 billion pounds at $1.90
B. Sell 60 billion pounds at $1.60
C. Sell 20 billion pounds at $1.90
D. Buy 10 billion pounds at $1.60
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose your expenses for this term are as follows:
tuition: $5,000, room and board: $3,000, books and other educational supplies: $500. Further, during the term, you can only work part-time and earn $4,000 instead of your full-time salary of $10,000. What is the opportunity cost of going to college this term, assuming that your room and board expenses would be the same even if you did not go to college? A) $5,500 B) $8,500 C) $11,500 D) $14,500
The way income is allocated among the population is called the
A) income curve. B) income spread. C) distribution of income. D) Gini allocation.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a. Part of the deadweight loss associated with monopoly is measured by the monopolist's economic profit. b. Marginal cost is always less than average total cost in a natural monopoly. c. Discount coupons available free to the public are a type of price discrimination. d. Anti-trust laws make it harder for firms to create synergies.
A minimum wage law (that sets the minimum wage above the equilibrium wage) can be expected to
A) clear the market for unskilled workers. B) increase the number of unskilled workers employed. C) increase the number of firms in those industries where the law is effective. D) reduce the number of unskilled workers employed and/or reduce the number of hours worked by unskilled workers. E) all of the above