The image of an object beneath the surface of a medium of refractive index n > 1 is seen in air by a person looking down on the surface. This image, formed by light rays leaving the flat refractive surface, is
a. real and closer to the viewer than the object.
b. virtual and closer to the viewer than the object.
c. real and farther from the viewer than the object.
d. virtual and farther from the viewer than the object.
e. virtual and the same distance from the viewer as the object.
b
You might also like to view...
Self-Inductance: An ideal solenoid has a self-inductance L. If you now double its radius and its length, but do not change the number of coils, what will its self-inductance be?
A. 4L B. 2L C. L D. L/2 E. L/4
The symbols 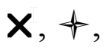 and
and  are used to represent, respectively, the charge density per unit
are used to represent, respectively, the charge density per unit
A. length, volume, and area. B. volume, length, and area. C. area, volume, and length. D. volume, area, and length. E. area, length, and volume.
How does the velocity of sound in air vary with the air temperature?
In which of the following cases would you expect degeneracy of the first excited state? Hint: Make sure to consider all three dimensions