Gravitational Potential Energy: An 825-kg space vehicle is circling Earth in a circular orbit with a radius of 10,300 km. Its orbit is to be changed to a larger circle with a radius of 17,400 km. How much energy is required to accomplish this? The mass of Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2.
A. 1.00 × 109 J
B. 1.30 × 1010 J
C. 6.51 × 109 J
D. 4.45 × 109 J
E. 4.50 × 1010 J
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A cantilever wood pole carries force P 5 300 N applied at its free end, as well as its own weight (weight density 5 6 kN/m3). The length of the pole is L 5 0.75 m and the allowable bending stress is 14 MPa. The required diameter of the pole is approximately:
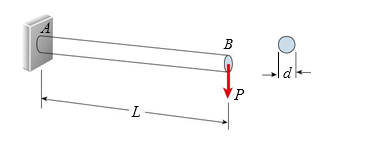
(A) 4.2 cm
(B) 5.5 cm
(C) 6.1 cm
(D) 8.5 cm
Unpolarized light of intensity Io passed through a Polaroid sheet with its polarizing axis at the 12 o'clock position and then through a second with its polarizing axis at the 1 o'clock position. What is the intensity of the emerging light?
What will be an ideal response?
In what way(s) has Pluto long been known to be different from the planets?
A) Its orbit is more inclined to the ecliptic plane. B) It is composed primarily of ices. C) It is far smaller than the terrestrial planets. D) It has a highly eccentric orbit. E) All of the above
Four identical particles (mass of each = 0.40 kg) are placed at the vertices of a rectangle (2.5 m × 4.0 m) and held in those positions by four light rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia of this rigid body about an axis that passes through the mid-points of the shorter sides and is parallel to the longer sides?
a. 2.2 kg/m2 b. 2.8 kg/m2 c. 2.5 kg/m2 d. 3.1 kg/m2 e. 1.6 kg/m2