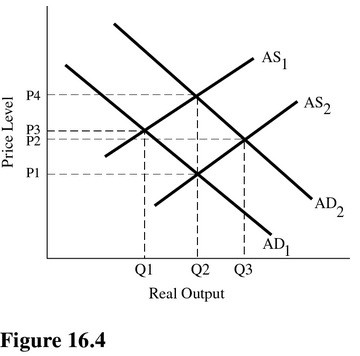
 Refer to Figure 16.4. If the economy is initially in equilibrium at P3 and Q1, the appropriate policy to move the economy to an equilibrium at P1 and Q2 would be to
Refer to Figure 16.4. If the economy is initially in equilibrium at P3 and Q1, the appropriate policy to move the economy to an equilibrium at P1 and Q2 would be to
A. Increase government regulation.
B. Increase the marginal tax rate.
C. Increase the minimum wage rate.
D. Increase the investment in human capital.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Economists Kenneth Chay and Michael Greenstone found that in the two years following the passage of the Clean Air Act of 1970, the sharp reduction in air pollution also led to a decline in infant deaths
Although this and other studies provide compelling evidence of the link between pollution and infant health, it is not clear that reductions from the much lower levels of ambient pollution today would have the same effect. Which of the following reasons could explain this? A) Today, the level of pollution is much higher. Therefore, it will take a much larger reduction in air pollution to reap benefits similar to those in 1970. B) The cost of pollution abatement today is much higher than it was in the 1970s. Thus, it would be far more costly to achieve the same level of benefit today as the benefit achieved in 1970. C) When levels of pollution are high, the marginal benefit of reducing pollution is low. Therefore, it was necessary to significantly reduce air pollution in 1970 before benefits could be realized. Today, when the level of pollution is much lower, such drastic measures are unnecessary. D) When levels of pollution are high, the marginal benefit of reducing pollution also is high. It follows therefore that the benefit of reducing air pollution in 1970 would be much higher than the benefit from a proportional reduction in air pollution today when the level of pollution is much lower.
A shift outward of the aggregate supply curve could be caused by
a. higher import prices. b. lower import prices. c. energy shortages. d. rising wage rates.
Which of the following best describes the response of output as time passes to an increase in the saving rate?
a. The growth rate of output does not change. b. The growth rate of output increases and gets even larger as time passes. c. The growth rate of output increases and does not change as time passes. d. The growth rate of output increases, but diminishes to its former level as time passes.
According to the substitution effect, a decrease in the price of a product leads to an increase in the quantity demanded because buyers:
A. purchase more complementary goods. B. purchase more substitute goods. C. purchase fewer substitute goods. D. have more real income.