Suppose that many households look to the stock market to gauge how the economy is likely to perform in the future
When stock prices are rising, then households will be optimistic about the future state of the economy and will increase their spending on houses and consumer durables, such as cars and furniture. When stock prices are falling, then households will be pessimistic about the future and will cut back on their spending. If this view of the link between stock prices and household spending is correct, then what will be the effect of a decline in stock prices on output in the new Keynesian view? Be sure to distinguish the short run from the long run.
The fall in stock prices will reduce household spending and shift the AD curve to the left. In the short run, output falls. In the long run, SRAS shifts to the right. As a result, the price level falls to restore equilibrium at the full employment level of output.
You might also like to view...
If aggregated demand is less than actual output, unplanned inventory ________ will cause output to ________
A) accumulation; rise B) depletion; fall C) depletion; rise D) accumulation; fall
To find its profit-maximizing output level, a firm should operate where
A. AVC = MC. B. MC = MR. C. TFC = TVC. D. AFC = AVC.
Refer to the table below. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant) average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 23rd cake in inventory?
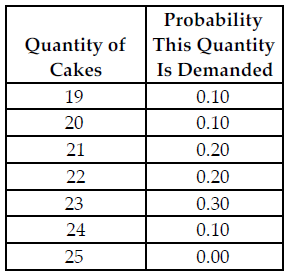
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) $3.20
B) $8.00
C) $4.80
D) $8.20
Nearly _____________ of the world's people have never made a phone call.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).