Consider a competitive industry and a price-taking firm that produces in that industry. The market demand and supply functions are estimated to be: Demand: Qd = 10,000 ? 10,000P + 1.0MSupply: Qs = 80,000 + 10,000P ? 4,000PIwhere Q is quantity, P is the price of the product, M is income, and PI is the input price. The manager of the perfectly competitive firm uses time-seris data to obtain the following forecasted values of M and PI for 2015: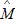 = $50,000 and
= $50,000 and 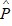 I = $20The manager also estimates the average variable cost function to beAVC = 3.0 ?
I = $20The manager also estimates the average variable cost function to beAVC = 3.0 ?
0.0027Q + 0.0000009Q2Total fixed costs will be $2,000 in 2015. The profit (loss) is
A. $2,600
B. $4,000
C. $2,000
D. $3,250
E. none of the above
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Governments contribute to increased average labor productivity in each of the following ways except by:
A. allowing the free and open exchange of ideas. B. maintaining political stability. C. imposing taxes on wages. D. establishing well-defined property rights.
If a 6 percent decrease in the price leads to a 5 percent increase in the quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand is
A) 0.30. B) 0.60. C) 0.83. D) 1.20.
An indication to the Open Market Account Manager that commercial banks are experiencing a liquidity surplus would be a
A) falling federal funds rate. B) rising federal funds rate. C) falling discount rate. D) rising discount rate.
Figure 17-12
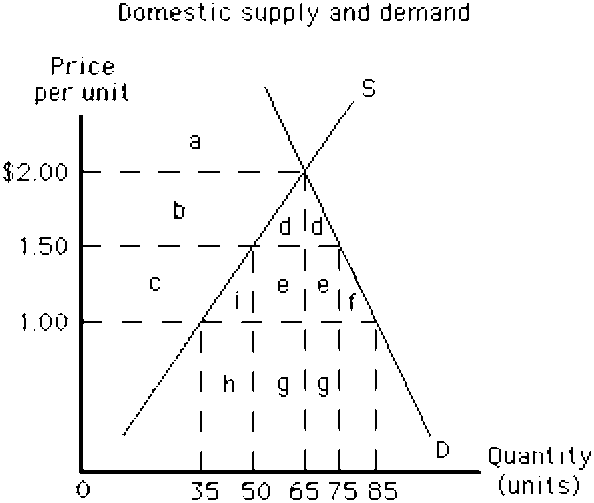
At a world price of $1.00 in ,
a.
20 units will be exported
b.
20 units will be imported
c.
50 units will be exported
d.
50 units will be imported
e.
10 units will be exported