How do taxes work to reduce a negative externality? Explain in detail
What will be an ideal response?
If a per-unit tax exactly equal to marginal damage costs is imposed on a firm, the firm will weigh the tax, and thus the damage costs, in its decisions. At the new equilibrium price consumers will be paying an amount sufficient to cover full resource costs as well as the cost of damage imposed. The efficient level of output for the firm will also fall as well.
You might also like to view...
Monetary aggregates are
A) measures of the money supply reported by the Federal Reserve. B) measures of the wealth of individuals. C) never redefined since "money" never changes. D) reported by the Treasury Department annually.
When taxes decrease, consumption
a. decreases as shown by a movement to the left along a given aggregate-demand curve. b. decreases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left. c. increases as shown by a movement to the right along a given aggregate-demand curve. d. increases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.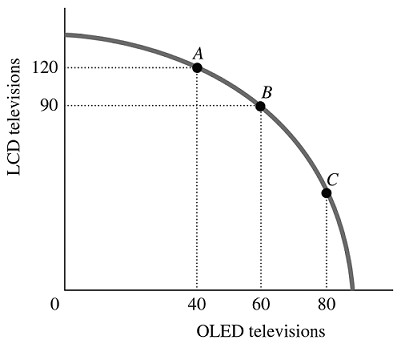 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The marginal rate of transformation in moving from Point A to Point B is
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The marginal rate of transformation in moving from Point A to Point B is
A. -2/3. B. -1.5. C. -3. D. -30.
In the last few decades, the poverty rate in the US has
A. changed little. B. decreased. C. increased. D. may have increased or decreased, we do not know for certain.