With a constant opportunity cost between goods A and B, the PPF for goods A and B would
A) be a straight line.
B) be a bowed-outward line.
C) be a bowed-inward line.
D) not exist.
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following would cause the demand for labor to change?
a. c and e. b. A change in the cost of living. c. Changes in the wage rate. d. Movements along the labor demand curve. e. A change in the price of the good produced.
Figure (a) represents the domestic demand and supply of televisions. Suppose free trade is allowed and the current world price of televisions is P1 as shown in Figure (b). Now suppose the domestic government imposes a tariff increasing the domestic price to P2 in Figure (b). This tariff will cause
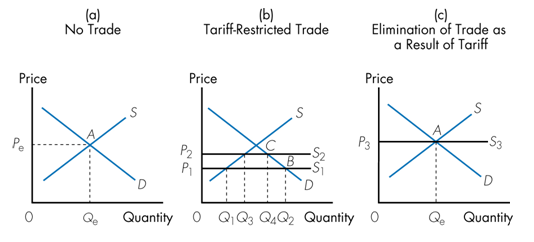
a. imports to fall from Q2 minus Q1 to Q4 minus Q3.
b. domestic producers to increase their production from Q1 to Q3.
c. domestic consumers to reduce their consumption from Q2 to Q4.
d. All of the above.
The __________ Act protects employee rights and the __________ Act protects employer rights.
A. Wagner; Taft-Hartley B. Taft-Hartley; Wagner C. Sherman Antitrust; Wagner D. Taft-Hartley; Landrum-Griffin
Suppose the marginal product of labor is MPN = 200 - 0.5Nwhere N is aggregate employment. The aggregate quantity of labor supplied is 300 + 8w, where w is the real wage. If a supply shock increases the marginal product of labor by 10 (to MPN = 210 - 0.5 N), by how much does the real wage increase?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4