If producing a good or a service creates pollution, then
A) an unregulated competitive market produces an efficient output.
B) the industry's supply curve includes the extra cost of pollution.
C) at the unregulated, competitive market equilibrium quantity, marginal social cost is greater than the equilibrium price.
D) at the unregulated, competitive market equilibrium quantity, marginal social benefit and marginal social cost are equal.
E) at the unregulated, competitive market equilibrium quantity, marginal social benefit is less than the equilibrium price.
C
You might also like to view...
A firm in monopolistic competition can determine what price to charge for its product because of
A) barriers to entry. B) economies of scale. C) product differentiation. D) the fact there are many buyers.
If the effective rate of protection is greater than the nominal rate of protection, there must be tariffs on intermediate products
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The above figure shows the market for steel ingots. The socially optimal quantity of steel is
A) 0 units. B) 50 units. C) 100 units. D) produced if the market were competitive.
Figure 17-10
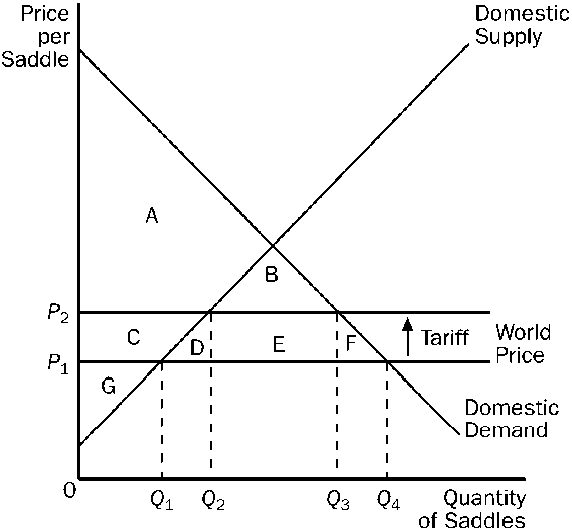
Refer to . Consumer surplus with the tariff is
a.
A.
b.
A + B.
c.
A + C + G.
d.
A + B + C + D +E + F.