The following quote is taken from a university extension publication for farmers:
"Grain poisoning, also known as grain overload or lactic acidosis, is usually the result of stock consuming large quantities of grain or pellets to which they are unaccustomed. Pasture-fed cows or feedlot cattle not yet adapted to grain may become acutely ill or die after eating only moderate amounts of grain, whereas stock accustomed to diets high in grain content may consume large amounts of grain with little or no effect."
What is happening in the digestive system of the livestock that causes grain poisoning and why does a gradual shift in diet avoid this problem?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: A major shift in diet, where the rumen flora must suddenly ferment a different substrate, results in different products formed. When ruminant animals suddenly consume grain instead of grass, the starch in the grain causes Streptococcus bovis to grow and produce large quantities of lactic acid. Lactic acid is a stronger acid than other volatile fatty acids that are usually produced (e.g., butyric and proprionic acid). When the pH of the rumen decreases, blood acidosis can ensue (which can be lethal). If the ruminant switches slowly to a grain diet, the fermentative bacteria in the rumen adapt and bacteria that produce the normal fatty acids are selected for allowing rumen functions to continue normally.
You might also like to view...
Examples of mollusks that live on land are the
A. earthworms. B. land crabs. C. mussels. D. scorpions. E. snails and slugs.
What type of cell signaling occurs through the extracellular matrix to nearby target cells?
What will be an ideal response?
The 2003 outbreak of SARS began in
a. the United States. b. Great Britain. c. Russia. d. Africa. e. China.
The A159E mutation causes an A amino acid to be replaced with an E amino acid (their structures are shown here). What effects do you think the A159E mutation will have on the troponin protein?
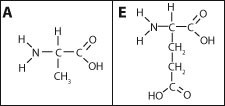
A) The mutation will not affect troponin function since both the A and E amino acids are hydrophobic and thus the troponin structure will not be affected.
B) The mutation will probably make troponin more stable at low pH and at higher temperatures since the E amino acid is acidic.
C) Since the E amino acid is hydrophilic, it will try to be exposed on the surface of the protein and thus will disrupt the tertiary structure and potentially the function of troponin.
D) If the A amino acid is replaced by the basic E amino acid, then the secondary and tertiary structures will be affected and troponin will likely not fold correctly.