Calorimetry: A 90-g aluminum calorimeter contains 390 g of water at an equilibrium temperature of 20°C. A 160-g piece of metal, initially at 305°C, is added to the calorimeter. The final temperature at equilibrium is 32°C. Assume there is no external heat exchange. The specific heat capacities of aluminum and water are 910 J/kg ? K (aluminum) and 4190 J/kg ? K (water). What is the specific heat capacity of the 160-g piece of metal?
A. 470 J/kg ? K
B. 430 J/kg ? K
C. 350 J/kg ? K
D. 310 J/kg ? K
E. 510 J/kg ? K
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Addition by 1. Components: Displacement vector src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__cp1pbb0313192044__f15g1q11g5.jpg" style="vertical-align: -5.0px;" />.(c) Determine the x and y components of vector 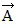 is 75 cm long and points at 30° above the +x-axis. Displacement vector
is 75 cm long and points at 30° above the +x-axis. Displacement vector 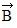 is 25 cm long and points along the -x-axis. Displacement vector
is 25 cm long and points along the -x-axis. Displacement vector 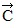 is 40 cm long and points at 45° below the -x-axis.(a) Determine the x and y components of vector
is 40 cm long and points at 45° below the -x-axis.(a) Determine the x and y components of vector 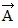 .(b) Determine the x and y components of vector
.(b) Determine the x and y components of vector 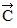 .(d) Determine the x and y components of the resultant of these three vectors.(e) Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant of these three vectors.
.(d) Determine the x and y components of the resultant of these three vectors.(e) Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant of these three vectors.
What will be an ideal response?
Iced tea is made by adding ice to 3.0 kg of hot tea, initially at 80°C. How many kg of ice, initially at 0°C, are required to bring the mixture to 10°C? (Lf = 3.33 x 105 J/kg, cw = 4186 J/kg•°C)
a. 2.8 kg c. 1.4 kg b. 1.6 kg d. 2.3 kg
It takes 87 J of work to stretch an ideal spring from 1.4 m to 2.9 m from equilibrium. What is the value of the spring constant (force constant) of this spring?
A) 52 N/m B) 77 N/m C) 39 N/m D) 27 N/m
A metallic coin is given a positive electric charge. Its mass:
1.increases measurably. 2.increases by an amount too small to measure directly. 3.remains unchanged. 4.decreases by an amount too small to measure directly. 5.decreases measurably.