Rachel babysits for her sister for no pay. When she babysits for someone else she charges $8 an hour. When is Rachel's babysitting included in GDP?
a. When she babysits for her sister and when she babysits for someone else.
b. When she babysits for her sister, but not when she babysits for someone else.
c. When she babysits for someone else, but not when she babysits for her sister.
d. Neither when she babysits for her sister nor for someone else.
Answer: c. When she babysits for someone else, but not when she babysits for her sister.
You might also like to view...
A tariff:
A. is a tax on imports. B. is a tax on exports. C. directly limits the total quantity of a good that can be imported. D. directly limits the total quantity of a good that can be exported.
Risk pooling:
A. assures the individuals that they are less likely to have a catastrophe occur. B. reduces the risk of catastrophes happening collectively to groups. C. doesn't reduce the chances of catastrophes happening to individuals. D. None of these statements is true.
Refer to the graph shown. If this monopolist produces 45 units of output per day, it will: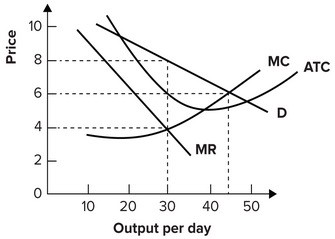
A. charge a price that exceeds its marginal cost. B. be maximizing profit. C. be able to increase profit by producing more per day. D. be able to increase profit by producing less per day.
Which of the following measurement issues makes interpretation of U.S. poverty rates difficult?
A. Poverty statistics measure consumption rather than income, and some families may receive income that is above the official poverty line. B. The high cost of living in urban areas tends to result in the understatement of poverty. C. Most people below the poverty line have substantial unreported income. D. The poverty rate is adjusted for every urban and rural area, so people's poverty status changes whenever they move.