Refer to the graph shown. Assume the market is initially in equilibrium at point j in the graph but the imposition of a per-unit tax on this product shifts the supply curve up from S0 to S1. The effect of the tax is to raise equilibrium price from: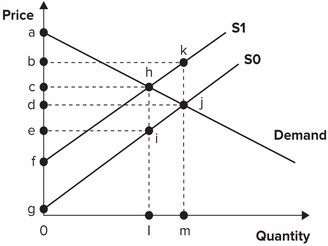
A. c to b.
B. d to b.
C. e to c.
D. d to c.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
What is the distinction between a money price and a relative price?
What will be an ideal response?
To maintain a price below the equilibrium price,
a. demand must increase. b. supply must increase. c. the government must set a ceiling price. d. supply must decrease.
In the new Keynesian model, the ultimate effect on inflation of an anticipated aggregate demand shock is ________
A) less than if that event was unanticipated B) greater than if that event was unanticipated C) the same as would develop if that event had never occurred D) independent of whether or not that event is anticipated or unanticipated
Under a fixed exchange rate system, the central bank must
a. have an unlimited supply of domestic currency. b. have a very large supply of foreign assets. c. follow a constant money growth rule. d. allow the money supply to adjust to keep interest rates and exchange rates unchanged.