The profit-maximizing output of a pure monopoly is not socially optimal because in equilibrium:
A. price equals minimum average total cost.
B. marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C. marginal cost exceeds price.
D. price exceeds marginal cost.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
According the graph shown, if this economy were open to free trade, it would:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as the world price for that good.
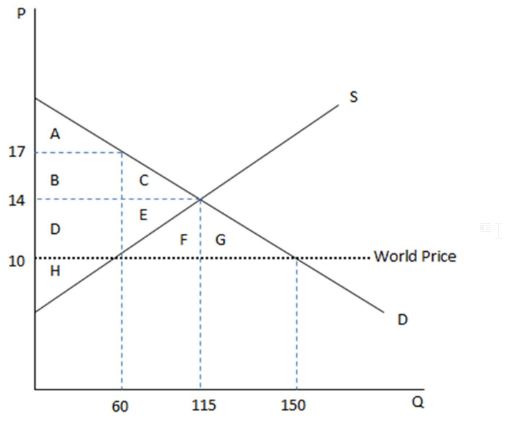
A. import this good, because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
B. export this good, because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
C. import this good, because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
D. export this good, because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
As the price of gasoline rose during the 1970s, consumers cut back on their use of gasoline relative to other consumer goods. This situation contributed to which bias in the consumer price index?
a. Substitution bias. b. Transportation bias. c. Quality bias. d. Indexing bias.
The typical welfare family consists of a ____________ and ____________ children.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The following data show the relationship between the number of drivers who leave for work at 8 a.m., their average commute time, and their marginal benefit of commuting.Number of DriversWho Leave at 8 a.m.AverageCommute TimeMarginalBenefit10030 minutes$1020065 minutes$8300110 minutes$4400170 minutes$3500260 minutes$1 If there is no charge to use the highway, then one would expect that ________ than the socially optimal number of drivers will leave at 8 a.m. because ________.
A. less; each driver's use of the highway imposes an external cost on other drivers by increasing the commute time B. more; each driver's use of the highway imposes an external cost on other drivers by increasing the commute time C. more; the social marginal benefit of using the highway is greater than the private marginal benefit D. less; the private marginal benefit of using the highway is greater than the social marginal benefit