Exhibit 8-19 Long-run perfectly competitive industry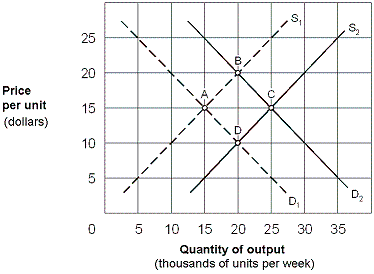
As shown in Exhibit 8-19, assume that a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium at point A. If the demand curve shifts from D1 to D2, the adjustment sequence between points will be:
A. A to B, then back to A.
B. A to D, then back to A.
C. A to D, then to C.
D. A to B, then to C.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Voluntary exchange
A. is usually beneficial to one party, but not the other. B. is always beneficial to both parties. C. is occasionally beneficial to both parties. D. occurs only between nations, not between individuals.
Increased production, but not increased inflation, will result in higher:
A. nominal GDP. B. money GDP. C. real GDP. D. current dollar GDP.
Increased specialization in large firms might lead to:
A. upward-sloping marginal cost curves. B. horizontal marginal cost curves. C. downward-sloping long-run average cost curves. D. upward-sloping long-run average cost curves.
Consumers' ability to purchase a good or service is limited by:
A. their income only. B. the prices for the goods or services only. C. both the prices for the goods and services and their income. D. their preferences.