Briefly describe classical complement activation and cell damage
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: Classical activation of complement occurs when IgG or IgM antibodies bind (fix) antigens, especially on cells surfaces. The complement proteins act in a defined sequence with activation of one complement component leading to the activation of the next, and so on. Cl components (Clq, Clr, and Cls) then bind to the antibody-antigen complex, leading to C4-C2 deposition on at an adjacent membrane site. This complex is a C3 convertase, an enzyme that cleaves C3 to C3a and C3b. The C3b cleavage product then binds to the convertase, forming a complex that initiates a C5-C6-C7 interaction at a second membrane site. C8 and C9 are then deposited with the C5-C6-C7 complex, resulting in membrane damage and cell lysis.
You might also like to view...
Most fungal spores are ____ reproductive cells that are produced ____
a. motile; sexually only b. motile; asexually only c. nonmotile; sexually only d. nonmotile; asexually only e. nonmotile; sexually or asexually
Which type of molecule is most likely to defuse across the plasma membrane?
a. small and lipid soluble b. small and water soluble c. large and lipid soluble d. large and water soluble
Suppose scientists discovered an organism that had a head with a brain at the anterior end of the dorsal nerve, eyes and other sensory organs, a skull, and a vertebral column. The organism could not be a/an
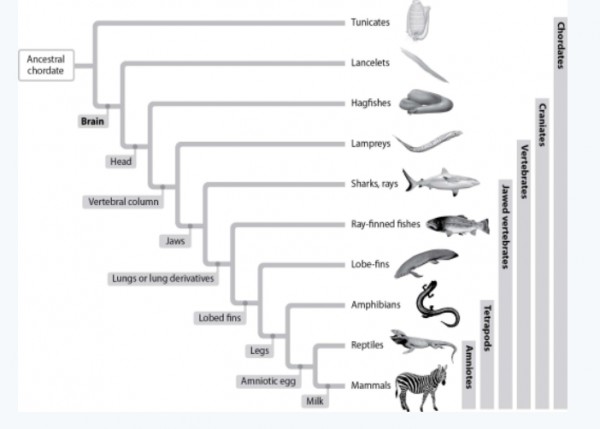
A) lamprey.
B) hagfish.
C) ray-finned shark.
D) amphibian.
Exons in mRNAs are excised and left in the nucleus.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)