Figure 18-2
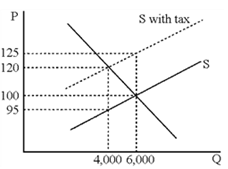
Figure 18-2 shows the widget market before and after an excise tax is imposed. What percentage of the tax per widget is borne by consumers, considering the true economic incidence of the tax?
A. 0 percent
B. 20 percent
C. 50 percent
D. 80 percent
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Nicholas does not possess marketable job skills; therefore, he is
A) frictionally unemployed. B) structurally unemployed. C) cyclically unemployed. D) seasonally unemployed.
Behavioral assumptions
a. make economic models more complex than if these assumptions were removed b. pertain only to consumers c. hold all other things constant d. are ways to test a hypothesis e. describe how individuals are expected to behave
The full-employment level of real GDP is the level which can be produced with: a. given technology and productive resources
b. frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero. c. cyclical unemployment equal to zero. d. both a and b. e. both a and c.
Suppose the tax amount on the first $10,000 income is $0; $2000 on the next $20,000; $4000 on the next $20,000; $6000 on the next $30,000; and 40 percent on any income over $80,000. Family A has income of $30,000 and Family B has income of $80,000. What
is the marginal and average tax rate for each family? A) Family A: marginal—10 percent; average—6.7 percent; Family B: marginal—30 percent; average—15 percent. B) Family A: marginal—10 percent; average—20 percent; Family B: marginal—30 percent; average—23 percent. C) Family A: marginal—10 percent; average—10 percent; Family B: marginal—40 percent; average—40 percent. D) Family A: marginal—10 percent; average—15 percent; Family B: marginal—40 percent; average—20 percent.