Since classical economists believe that both V and Q are constants for an economy in short-run equilibrium, the equation of exchange becomes a theory in which:
a. the quantity of money explains prices.
b. the quantity of money explains velocity.
c. the quantity of money explains real GDP.
d. changes in M cause changes in V.
e. prices are never flexible
a
You might also like to view...
The benefits of economic growth are ________, while the costs of economic growth are ________.
A. increased output per person; less future consumption B. increased output per person; too small for concern C. more current consumption; less future consumption D. increased output per person; the consumption sacrificed in exchange for capital formation
The absolute value of the slope of an isocost line equals the ratio of
A) the marginal productivities of the two inputs. B) the prices of the two inputs. C) the quantities of the two inputs. D) the marginal utilities of the two inputs.
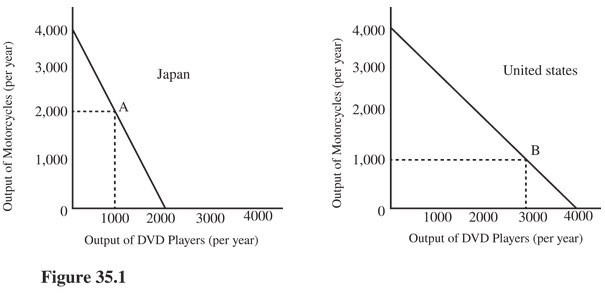 Compared to their initial positions at points A and B, as a result of complete specialization and trade, the output of the two countries added together in Figure 35.1 would result in an increase in
Compared to their initial positions at points A and B, as a result of complete specialization and trade, the output of the two countries added together in Figure 35.1 would result in an increase in
A. Neither DVD players nor motorcycles. B. Both DVD players and motorcycles. C. Motorcycles only. D. DVD players only.
A nonmonetary opportunity cost is called a(n) ________, while a cost that involves spending money is called a(n) ________.
A) implicit cost; explicit cost B) normal rate of return; asset C) accounting profit; economic profit D) accounting cost; explicit cost