A budget constraint shows
A) all of the combinations of sets of goods that yield the same level of satisfaction.
B) all of the possible combinations of goods that can be purchased with a specific budget.
C) all of the goods the consumer gets positive marginal utility from when the goods are consumed.
D) all of the goods that a consumer substitutes for other goods when prices fall.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
An increase in the duration of unemployment should be linked to a decrease in flows in and out of unemployment, if one is to keep unemployment constant
a. true b. false
If policymakers decrease aggregate demand, then in the short run the price level
a. falls and unemployment rises. b. and unemployment fall. c. and unemployment rise. d. rises and unemployment falls.
The table shows the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedule for a hypothetical economy.Real Domestic Output Demanded (in Billions)Price Level (Index Value)Real Domestic Output Supplied (in Billions)$3,000350$9,0004,0003008,0005,0002507,0006,0002006,0007,0001505,0008,0001004,000Refer to the above table. If the quantity of real domestic output demanded increased by $2000 at each price level, the new equilibrium price level and quantity of real domestic output would be:
A. 350 and $8000. B. 300 and $8000. C. 200 and $6000. D. 250 and $7000.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.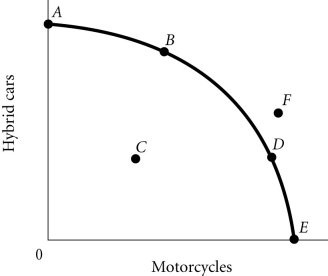 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
A. initially increases, then decreases. B. increases. C. remains constant. D. decreases.