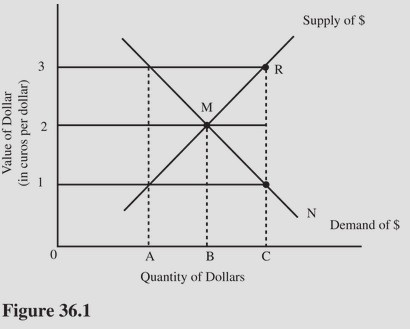
 Ceteris paribus, an increase in the U.S. demand for Greek goods in Figure 36.1 will
Ceteris paribus, an increase in the U.S. demand for Greek goods in Figure 36.1 will
A. Result in a movement from M to R on the supply curve for dollars.
B. Increase the dollar price of euros above $2 = 1 euro.
C. Make U.S. goods more expensive to Greek residents.
D. Result in a movement from M to N on the demand curve for dollars.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Henry, a perfectly competitive lime grower in Southern California, notices that the market price of limes is greater than his marginal cost. What should Henry do?
A) expand his output to increase profits B) shut down and incur a loss equal to his total fixed cost C) advertise his limes to be able to sell more output D) look for the output level where marginal revenue minus marginal cost is maximized E) shut down and earn no profit but also incur no loss
In Monetarist theory, the demand to hold money is:
a. The same as the demand to borrow real loanable funds. b. Upward sloping because as the real risk-free interest rate rises, people want to hold more money. c. Rather unstable because it changes greatly with movements in the real risk-free interest rate. d. Neutral, in the sense that it is independent from all macroeconomic variables. e. Rather stable and does not change greatly with movements in the real risk-free interest rate.
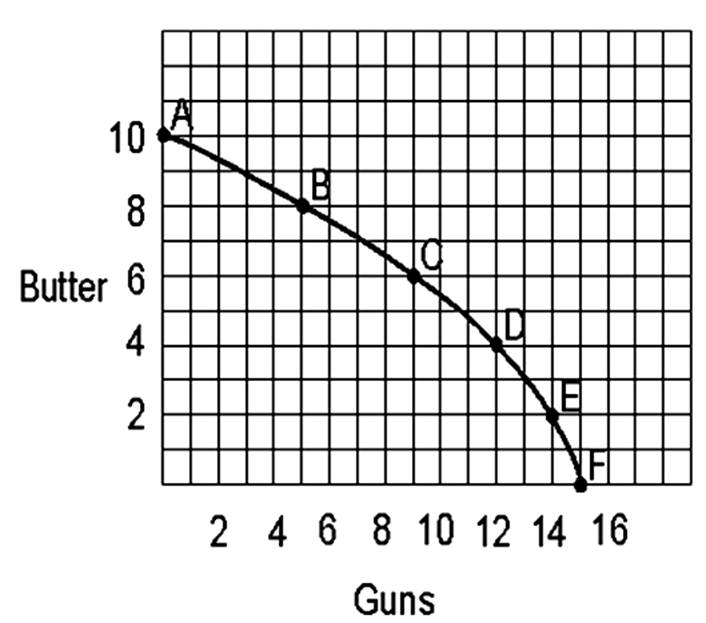
If point C is now 9 units of guns and 8 units of butter, the maximum units of guns possible to produce is 17 and the maximum units of butter possible to produce is 13, the production possibility curve would have shifted _____________ (outward/inward).
What are exchange rates? If a product cost 30 euros and the exchange rate was 1 euro = $1.50, then how much would the product cost in terms of U.S. dollars?
Please provide the best answer for the statement.