Imagine Tom's annual salary as an assistant store manager is $30,000, he owns a building that rents for $10,000 yearly, and his financial assets generate $1,000 per year in interest. One day, after deciding to be his own boss, he quits his job, evicts his tenants, and uses his financial assets to establish a bicycle repair shop. To run the business, he outlays $15,000 in cash to cover all the costs involved with running the business, and earns revenues of $50,000. What are Tom's accounting profits?
A. $50,000
B. -$6,000
C. $24,000
D. $35,000
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Implicit costs are usually easier to measure than explicit costs
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the table below. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant) average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 23rd cake in inventory?
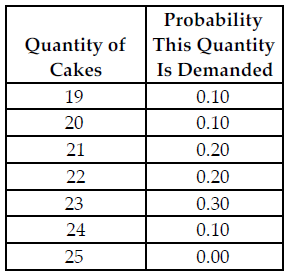
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) $3.20
B) $8.00
C) $4.80
D) $8.20
Which of the following is unique to perfect competition?
a. The individual firm cannot earn economic profit in the long run. b. It is easy for new firms to enter the industry. c. The market demand curve slopes downward. d. The demand curve facing an individual firm is perfectly elastic. e. The firms in the industry produce a homogeneous product.
Refer to Figure 21-10. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. If a consumer moves from bundle C to bundle A, her loss of cake cannot be compensated for by an increase in donuts. b. Because more is preferred to less, bundle C may be preferred to bundle E in some circumstances for this consumer. c. Bundle E is preferred to all other points identified in the figure. d. Even though bundle E has more of both goods than bundle B, we could draw a different set of indifference curves in which bundle B is preferred to bundle E.