In the long run, monopolistic competition
a. results in a monopoly
b. ends up with one firm, that is, competition transforms to monopoly
c. ends up with many firms in the industry
d. has zero barriers to entry
e. has no product differentiation
C
You might also like to view...
Explain carefully why the assumption of identical technology worldwide eliminates the classical basis for international trade
What will be an ideal response?
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. Someone with a low marginal propensity to consume probably has a low marginal propensity to save. 2. Equilibrium in the aggregate expenditure model requires that aggregate expenditure equals income. 3. According to the aggregate expenditure model, when aggregate expenditure is greater than output, output decreases. 4. Politics can affect aggregate expenditure. 5. Accounting for investment, government purchases, and net exports increases the autonomous portion of aggregate expenditure.
A surplus item is
A) the import of goods or services that is not needed by residents of a country. B) the import or export of products that are by-products of the manufacturing of export goods. C) any transaction that leads to a receipt by a resident of a country or its government. D) any transaction that leads to a payment by a resident of a country or its government.
Refer to the below table. What will be the economic profit or loss for this monopolistic ally competitive firm at the profit-maximizing level of output?
Answer the question based on the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistic ally competitive firm given in the table below.
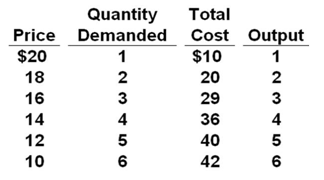
A. -$15
B. +$10
C. +$20
D. +$28