The RBC model tells us that
A) as the real wage rate rises, the amount of labor supplied and thus output produced falls.
B) as the price level rises, the real wage rises, thus raising the amounts of labor supplied and output produced.
C) as the real interest rate rises, the amount of labor supplied and thus output produced rises.
D) as the price level rises above the expected price level, actual output rises above the natural real GDP.
C
You might also like to view...
"Trade liberalization should precede capital account liberalization." Discuss
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
a. Individual firms have the power to set prices. b. Firms produce differentiated products. c. New firms can easily enter the market. d. There are only a few very large firms producing all output in the market.
In the graph for the consumption function, the 45-degree line
A. contains only a consumption component. B. represents both planned consumption and planned investment. C. reflects a decreasing APC as real disposable income rises. D. shows various combinations where planned consumption equals real disposable income.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 5.7 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
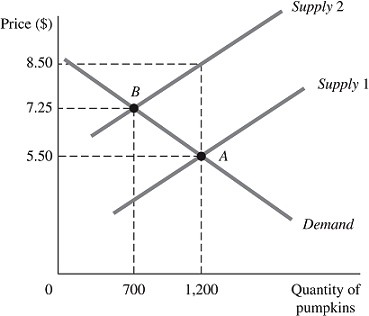 Figure 5.7The above figure represents the market for pumpkins both before and after the imposition of an excise tax, which is represented by the shift of the supply curve.Refer to Figure 5.7. Using the midpoint formula, the price elasticity of demand for pumpkins from the equilibrium point before the imposition of the tax to the equilibrium point after the imposition of the tax is
Figure 5.7The above figure represents the market for pumpkins both before and after the imposition of an excise tax, which is represented by the shift of the supply curve.Refer to Figure 5.7. Using the midpoint formula, the price elasticity of demand for pumpkins from the equilibrium point before the imposition of the tax to the equilibrium point after the imposition of the tax is
A. -0.02. B. -0.47. C. -2.11 D. -4.43