Suppose we know a particle’s four-momentum pt and px components. If we draw the particle’s four-momentum arrow on an energy–momentum diagram, we can use a hyperbola to determine
A. The particle’s energy.
B. The particle’s speed.
C. The particle’s x-velocity.
D. The particle’s momentum magnitude 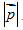 .
.
E. The particle’s mass.
F. The scaling on the t axis.
T. Something else (specify).
E. The particle’s mass.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not produced by plate tectonics?
a. midocean rifts b. rift valleys c. the ring of fire d. the Appalachian Mountains e. Earth's magnetic field
In an elastic collision, one ball has initial velocity v and strikes another, much less massive ball, that is initially at rest in a head-on collision. The velocity of the second ball after the collision is equal to:
A. v B. 2v C. v/2 D. -v E. something else
What is the source of the energy for the creation of heavy elements [heavier than iron]?
A) The shock of a supernova explosion. B) Fission. C) Helium fusion. D) Gravitational collapse. E) Hydrogen fusion.
Ball A is thrown up and Ball B is thrown down, both with the same initial speed. Neglecting air resistance, just prior to hitting the ground, which of the following is true?
1.You cannot tell which has the greater speed because it depends on the value of the initial speed. 2.Ball A's speed is greater than Ball B's speed. 3.They have the same speed. 4.Ball B's speed is greater than Ball A's speed.