When inflation rises, firms make
a. more frequent price changes. This raises their menu costs.
b. more frequent price changes. This reduces their menu costs.
c. less frequent price changes. This raises their menu costs.
d. less frequent price changes. This reduces their menu costs.
a
You might also like to view...
A firm has the production function 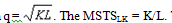 . The wage rate is $10 per unit of labor and the rental rate is $5 per unit of capital and the firm is going to spend $1000 on production.
. The wage rate is $10 per unit of labor and the rental rate is $5 per unit of capital and the firm is going to spend $1000 on production.
i. Assuming that the firm is free to choose any level of K and L to emply, how much of each should it emply? How much output will they produce? ii. Now assume that once the firm has chosen its level of L and K, the level of K becomes fixed. If the price of K increases to $8 per unit, how many units of output can the firm now produce if it spends the same amount? iii. Once the firm reaches the long run again and is able to vary its level of K, how much should L and K should it employ in order to achieve its original level of output? How much will that level of production cost?
Refer to Figure 28-2. Suppose the economy is at point A. The Fed uses expansionary monetary policy to lower the unemployment rate permanently below the level associated with A. Which of the following will occur?
A) Inflationary expectations will decline. B) Unemployment will rise above the natural rate. C) Unemployment will accelerate in the long run. D) Inflation will accelerate in the long run.
A major difference between stocks and bonds is that
A) bonds pay their owners dividends while stocks pay interest. B) bonds pay their owners interest while stocks pay dividends. C) the interest on a bond depends on the earnings of the corporation and is not guaranteed while dividends on stock are legally required. D) bonds represent ownership while stock represent debt.
Identify the correct statement
a. Between the 1960s and the 1990s, per capita GDPs grew faster in nonglobalizing countries. b. Between the 1960s and the 1990s, per capita GDPs grew faster in globalizing countries than in industrialized countries. c. Between the 1960s and the 1990s, per capita GDP growth rates in the industrialized world increased. d. Between the 1960s and the 1990s, per capita GDP in the industrialized world decreased. e. Between the 1960s and the 1990s, per capita GDP in all developing countries increased.