Comment on the following: "The problem with models like the Edgeworth Box and the Robinson Crusoe economy is that it is silly to assume competitive behavior when there are so few individuals in the market."
What will be an ideal response?
This is certainly true: Competitive behavior is price taking behavior -- and this price taking assumption is justified when economic agents are small relative to the economy. The criticism in the statement is therefore justified -- except that the purpose of the models is not to say that the competitive assumption is a good assumption to predict behavior in small settings. Rather, the intuitions in the Edgeworth Box (and the Robinson Crusoe economy) apply for large exchange economies (or large economies involving production) -- and in such economies, price taking behavior is in fact reasonable.
You might also like to view...
Why did India's economic growth rate lag far behind growth rates in South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan between 1960 and 1999?
A) Indian households saved too much and spent too little. B) Indian government officials opened the nation up to free international trade. C) India engaged in central economic planning. D) India has too small of a population to generate a highly specialized division of labor.
The Gallatin Plan (1808)
(a) was a plan by the U.S. Senate for a comprehensive system of internal land and water transport in the eastern part of the country to be built by the federal government. (b) was promoted on the basis that only the federal government could command sufficient resources to build a transportation system. (c) was partially implemented but not completed by the federal government because of concerns about the constitutionality of such federal action. (d) was characterized by all of the above.
When a shortage exists in a market, sellers
a. raise price, which increases quantity demanded and decreases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated. b. raise price, which decreases quantity demanded and increases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated. c. lower price, which increases quantity demanded and decreases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated. d. lower price, which decreases quantity demanded and increases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated.
Refer to the figure below. In the matrix above: 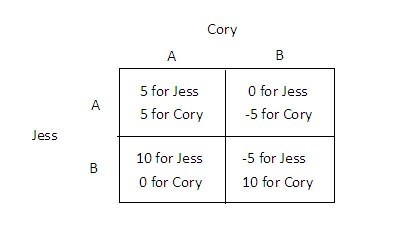
A. both Cory and Jess have the same dominant strategy. B. Cory has a dominant strategy, but Jess does not. C. neither Cory nor Jess has a dominant strategy. D. Jess has a dominant strategy, but Cory does not.