A pair of identical balls is connected by a massless rod, and thrown up into the air. The velocity of the center of mass is initially 17.2 m/s upward. 1.0 s later, one of the balls is measured to be at rest. What is the velocity of the other ball at this time? Ignore air resistance.
A. 14.8 m/s up
B. 9.8 m/s down
C. 7.4 m/s up
D. 7.4 m/s down
A. 14.8 m/s up
You might also like to view...
Light waves reflected off a body of water are strongly polarized in the horizontal direction. To reduce glare polarized sunglasses are made
A. with the transmission axis horizontal. B. with the transmission axis vertical. C. with the transmission axis at 37°. D. Polarized sunglasses don’t help with glare
Which of the following scenarios involves energy that we would typically calculate with Einstein's formula E=mc2?
A) A small amount of the hydrogen in of a nuclear bomb becomes energy as fusion converts the hydrogen to helium. B) An object accelerated to a great speed has a lot of kinetic energy. C) A mass raised to a great height has a lot of gravitational potential energy. D) A burning piece of wood produces light and heat, therefore giving off radiative and thermal energy.
A force of 500 N is applied to a rod with a diameter of 4.00 mm. The stress in the rod is
a. 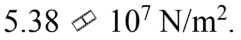
b. 
c. 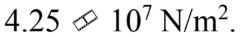
d. 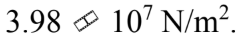
e. 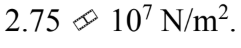
A 2.0-kg mass is projected vertically upward from ground level with an initial speed of 30 m/s. The mass rises to a maximum height of 35 m above ground level. What is the change in mechanical energy of the mass caused by air resistance between the point of projection and the point of maximum height?
a. -0.21 kJ b. -0.47 kJ c. -0.40 kJ d. -0.34 kJ e. -0.69 kJ