Which of the following is true of leakages and injections in the circular flow model?
a. Leakages minus injections equal gross domestic product (GDP)
b. Injections minus leakages equal gross domestic product (GDP).
c. Leakages minus injections equal zero in equilibrium.
d. Leakages must be less than injections for an economy to be in equilibrium.
e. Leakages must be greater than injections for an economy to be growing.
c
You might also like to view...
The basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply curve model helps explain
A) price fluctuations in an individual market. B) short-term fluctuations in real GDP and the price level. C) long-term growth. D) output fluctuations in an individual market.
Figure 4-9
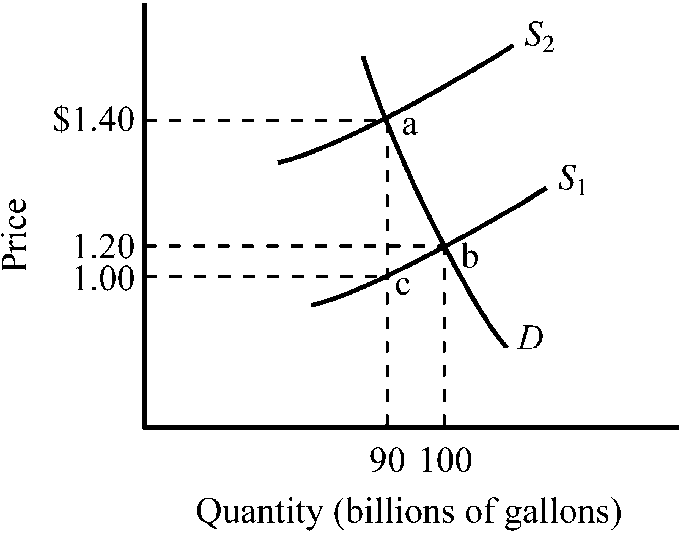
Refer to . The market for gasoline was initially in equilibrium at point b and a $.40 excise tax is illustrated. Which of the following states the actual burden of the tax?
a.
$.20 for buyers and $.20 for sellers
b.
$.30 for buyers and $.10 for sellers
c.
The entire $.40 falls on sellers.
d.
The entire $.40 falls on buyers.
Equilibrium price is the price:
a. from which there is always a tendency to move away b. where supply equals demand c. where there is either a surplus or a shortage d. suppliers agree to charge e. none of the above
Table 9-1 Output Consumption Investment Net Exports 1,000 800 500 100 1,500 1,200 500 100 2,000 1,600 500 100 2,500 2,000 500 100 3,000 2,400 500 100 3,500 2,800 500 100 4,000 3,200 500 100 ? In Table 9-1, at output of 4,000, inventories are
A. decreasing by 200. B. increasing by 200. C. increasing by 300. D. decreasing by 300.