Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
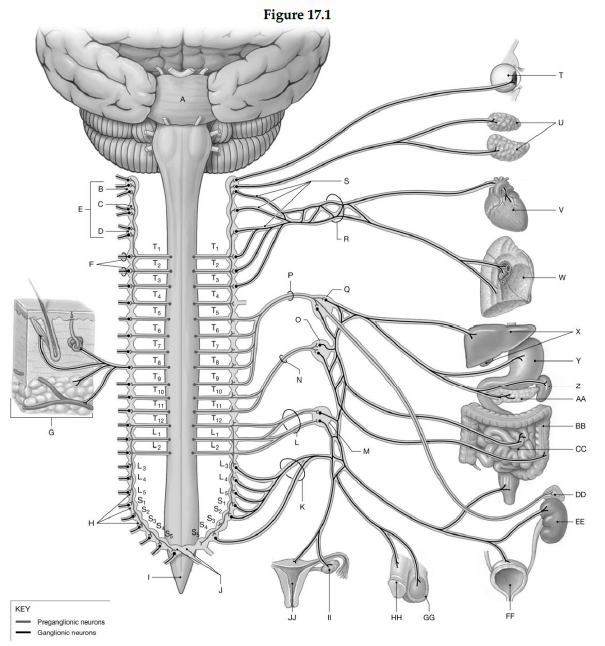
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
19) Label S: ______________________________
20) Label T: ______________________________
21) Label U: ______________________________
22) Label V: ______________________________
23) Label W: ______________________________
24) Label X: ______________________________
25) Label Y: ______________________________
26) Label Z: ______________________________
27) Label AA: ______________________________
28) Label BB: ______________________________
29) Label CC: ______________________________
30) Label DD: ______________________________
31) Label EE: ______________________________
32) Label FF: ______________________________
33) Label GG: ______________________________
34) Label HH: ______________________________
35) Label II: ______________________________
36) Label JJ: ______________________________
1) Pons
2) Superior cervical sympathetic ganglia
3) Middle cervical sympathetic ganglia
4) Inferior cervical sympathetic ganglia
5) Cervical sympathetic ganglia
6) Grey rami to spinal nerves
7) Postganglionic fibers to spinal nerves (innervating skin, blood vessels, sweat glands, arrector pili muscle, adipose tissue)
8) Sympathetic chain ganglia
9) Spinal cord
10) Coccygeal ganglia (Co1) fused together (ganglion impar)
11) Sacral splanchnic nerves
12) Lumbar splanchnic nerve
13) Inferior mesenteric ganglion
14) Lesser splanchnic nerve
15) Superior mesenteric ganglion
16) Greater splanchnic nerve
17) Celiac ganglion
18) Cardiac and pulmonary plexuses
19) Sympathetic nerves
20) Eye
21) Salivary glands
22) Heart
23) Lung
24) Liver and Gallbladder
25) Stomach
26) Spleen
27) Pancreas
28) Large intestine
29) Small intestine
30) Suprarenal medulla
31) Kidney
32) Urinary bladder
33) Scrotum
34) Penis
35) Ovary
36) Uterus
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. A loss of melanin in the skin leads to a condition called cyanosis. 2. The cells of the dermis are more tightly packed than the cells of the epidermis. 3. The arrector pili are tiny involuntary muscles in the dermis. 4. Eccrine glands reach full functioning before apocrine glands. 5. Pores in the skin are outlets for sebaceous glands.
Antineoplastics are safe to handle using usual methods
a. true b. false
Which of the following organelles contains digestive enzymes that destroy old, damaged organelles, harmful bacteria, viruses, and toxins?
A) Golgi apparatus B) lysosome C) ribosomes D) nucleus
If a person decided to jump over a chair, which of the following areas organizes the motor functions needed to carry out this action?
A. Premotor area B. Visual cortex C. Prefrontal area D. Auditory association area E. Visual association area