When looking at this graph for the welfare effects of a subsidy, c + g would equal ______.
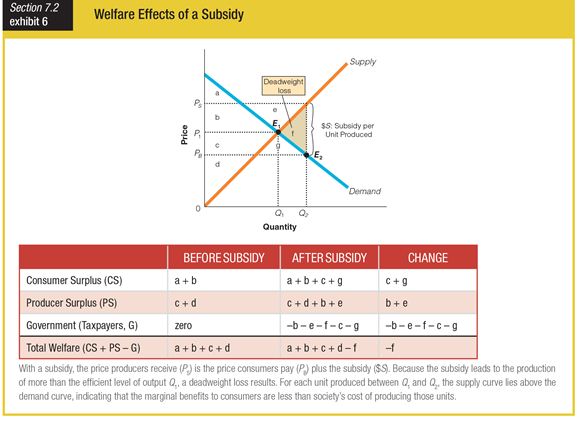
a. gains to the consumer
b. deadweight loss
c. cost to the taxpayers
d. total welfare gains
a. gains to the consumer
You might also like to view...
What would be the best description of what we assume about money prices in the short run?
A) Money prices of goods and services vary. B) Money prices of goods and services not related to each other. C) Money prices of goods are fixed. D) Money prices of services are fixed. E) Money prices of goods and services are only temporarily fixed.
Which of the following is likely to cause an outward shift of a production possibility curve?
a. An increase in the price of the commodity represented on the horizontal axis b. A fall in the cost of producing the commodity represented on the vertical axis c. An improvement in the available technology d. A fall in the supply of resources e. An increase in the supply of unskilled workers
Suppose the president of a college argues that a 25 percent tuition increase will raise revenues for the college. It can be concluded that the president thinks that demand to attend this college is:
a. unitary elastic. b. perfectly elastic. c. inelastic, but not perfectly inelastic. d. elastic.
Which of the following best explains how consumer spending can decrease even if disposable income remains the same?
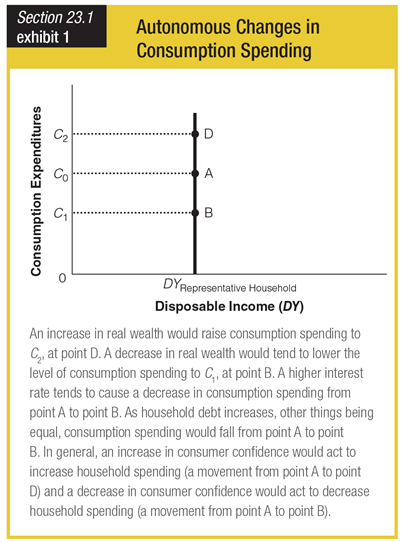
a. Supply may decrease, raising the price of many goods.
b. The value of the consumers’ assets, such as stocks or property, might rise.
c. Inflation reduces the purchasing power of consumers’ disposable income.
d. Higher interest rates cause an increase in saving and decrease in spending.