Explain how IMF conditionality has changed over time
What will be an ideal response?
Before the 1970s, IMF conditionality focused primarily on correcting the immediate source of the problem that led to a crisis, and it avoided involvement with underlying economic issues, such as trade policy and privatization. This approach was criticized as short-sighted, and it was agreed that the Fund should involve itself beyond short-run economic policy. New loan programs were developed to provide money and technical assistance to countries that needed help in restructuring their economies. This shift involved the IMF in far more than crisis resolution, as it took on an active role in assisting in privatization, the design of social policies, trade policy reform, agricultural policies, environmental policies, and a number of other areas. By the late 1990s, there was growing recognition that mission creep had become a problem and that the Fund had taken on responsibilities for which it is not suited, such as economic development in the long run. Several of the proposals for reforming the international financial architecture envision a reduced role for the IMF, particularly in the area of long term economic development.
You might also like to view...
Looking at the table above, real wages ________ from 2011 to 2012, and real wages ________ from 2012 to 2013.
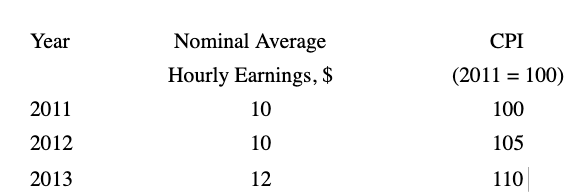
A) fell; rose
B) fell; fell
C) rose; fell
D) rose; rose
A company could produce 99 units of a good for $316 or produce 100 units of the same good for $320. The marginal cost of the 100th unit
A) is $3.20. B) is $4.00. C) is $320. D) cannot be calculated with this information.
In perfect competition, firms enter the market whenever the market price exceeds the minimum average variable cost
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In the classical model, what happens to the level of real GDP if aggregate demand increases?
A. Real GDP would increase at first, then decrease. B. Real GDP decreases. C. Real GDP increases. D. Real GDP would remain the same, at equilibrium.